5 Ways to Minimize the Risk of Cyberattacks
blog/5-ways-to-minimize-risk-of-cyberattacks
2024-05-10
With cybersecurity fresh in mind for most of Western Canada after the recent data breaches of London Drugs and BC Libraries Cooperative, it’s a great time to talk about some of the safety practices that can help prevent data breaches and cybersecurity attacks.
Big corporations almost always have IT people or consultancies telling them when their systems are at risk of cyber-attacks, compatibility issues, or generally decreased productivity due to a hardware/software performance.
Smaller companies don’t generally have that luxury of knowing, planning for, or generally being aware of all of the assets under their belt (unless they have a comprehensive asset management system).
In the case of London Drugs; while specific details have not yet been released to the public, their data breach incident lead to all 79 Canadian locations being shut down for at least 6 days (some stayed closed for longer).
The ITRC reports that by the end of 2022, there were 374,992,920 victims of cyberattacks who had personal data stolen; the amount of victims is accredited to the 1,595 cyberattack breaches that year.
Additionally, system and human errors make up for an additional 151 data breached that year, adding another 24,130,504 people to the victims list of 2022.
With that in mind, here are 5 things that you can do to prevent data breaches and improve your overall cybersecurity.
1. Update Outdated Technology
Average IT System Lifespan in Institutions; visualizing how long a system is kept before being decommissioned (via: Listed Tech)
Outdated software and systems present significant security vulnerabilities for businesses.
Running on obsolete platforms or using software with unpatched vulnerabilities exposes organizations to the risk of cyberattacks.
Hackers often exploit known security flaws in outdated software to gain unauthorized access, steal sensitive information, or disrupt operations.
Therefore, it is crucial for businesses to regularly update their software and systems with the latest security patches and fixes, and replace legacy systems that no longer meet current security standards or cannot be adequately supported by vendors.
The image above showcases a trend in Institutions: an increasingly faster software decommissioning over a span 27 years.
The same source reports that 66% of systems within an Institutions’ technology stack has a life span of less than 10 years.
2. MFA Authentication Practices
10 Best Practices for MFA (via: ToolBox)
Weak authentication practices, such as inadequate password policies and the absence of multi-factor authentication (MFA), make it easier for attackers to compromise user accounts and gain unauthorized access to critical systems and data.
Businesses should enforce strong password policies that require complex passwords and regular password changes.
Additionally, implementing MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide additional verification factors before accessing sensitive resources.
A good MFA practice involves using a combination of factors such as, SMS codes, email codes, authenticator apps, or hardware tokens to drastically improve the security of any given software.
3. Reduce Human Error and Promote Cybersecurity Awareness
Top Cyber Security Training Topics (via: TechTarget)
Human error and lack of cybersecurity awareness among employees pose significant security risks to businesses.
Phishing attacks, social engineering tactics, and inadvertent data disclosures can all result from employees falling prey to cyber threats.
Therefore, organizations must invest in comprehensive cybersecurity training and awareness programs to educate employees about common cyber risks and teach them how to recognize and respond to potential threats effectively.
Some companies include cybersecurity training during the onboarding process, along with mandatory cybersecurity refreshment courses periodically.
These onboarding programs are designed to help employees understand the proper procedures for suspicious emails, who to contact, etc.
4. Strong Data Protection Measures
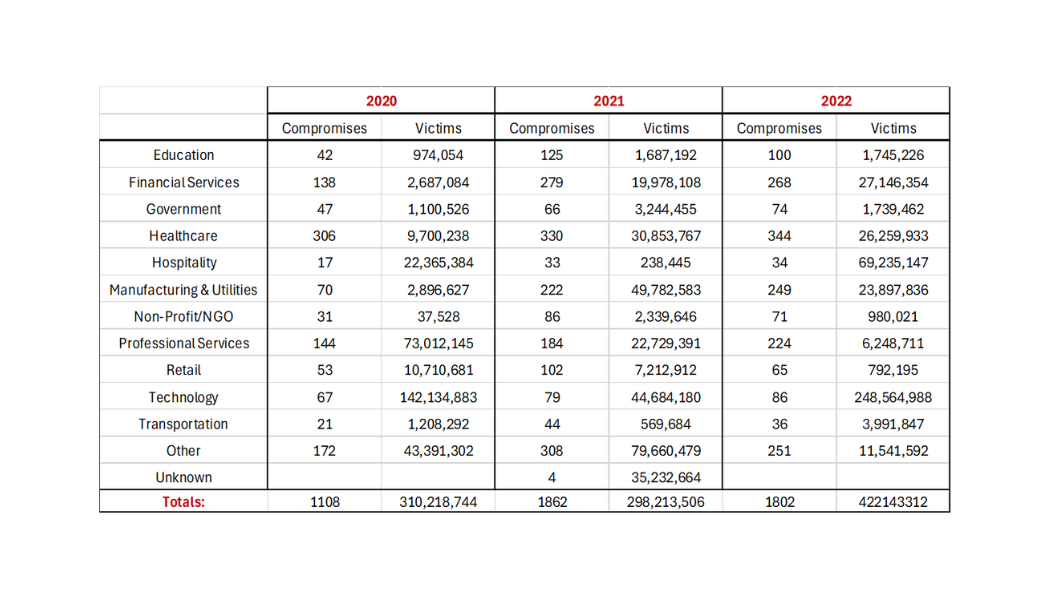
Data Breach Compromises by Industry (via: ITRC)
Inadequate data protection measures leave businesses vulnerable to data breaches and compliance violations.
It was reported by ITRC that were 1802 publicly reported organizational data breaches in the United States.
Failure to encrypt sensitive data, both in transit and at rest, increases the risk of unauthorized access and data theft.
To protect confidential information from interception and unauthorized disclosure, companies can either implement encryption technologies within their technology stack or use software that has advanced security typically vendors who are complaint with local laws).
Additionally, establishing proper access controls, monitoring user activity, and conducting regular security audits can help identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
5. Supply Chain Security Assessments
7 Best Practices to Solve Supply Chain Security Problems (via: Ekran System)
Supply chain vulnerabilities are a growing concern for businesses, particularly as organizations increasingly rely on third-party vendors and partners for various products and services.
Supply chain attacks, such as software supply chain compromises or vendor security breaches, can have far-reaching consequences for businesses, including data breaches, financial losses, and reputational damage.
To mitigate supply chain risks, businesses should assess the security practices of their vendors, implement vendor risk management processes, and establish clear contractual agreements regarding security requirements and responsibilities.
What Else Can You Do to Prevent Cyberattacks?
Conduct Regular Security Audits*
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Regularly Update Software (and turn on automatic updates on your operating system)
Educate Employees on Cybersecurity*
Enforce Strong Password Policies*
Deploy Firewalls and Intrusion Detection Systems
Encrypt Sensitive Data in Transit and at Rest
Backup Data Regularly
Establish Incident Response Plans*
Limit Access to Sensitive Information
*Need a way to plan, track, and organize these initiatives? Let’s talk about SmartSuite.